Introduction
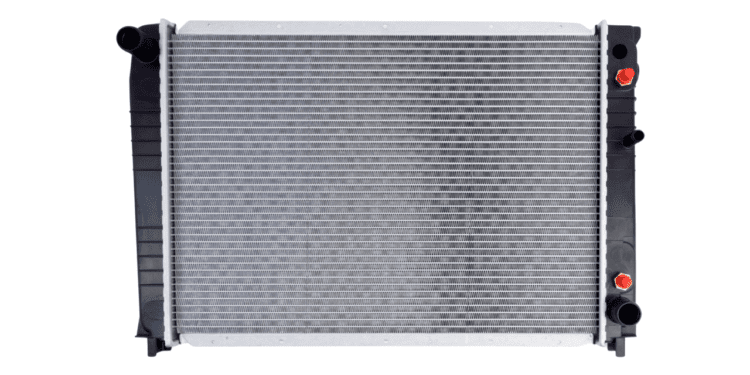
Car radiators play a crucial role in keeping your vehicle’s engine cool and running smoothly. Understanding how they work, how to maintain them, and when to repair or replace them is essential for every car owner. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into all aspects of car radiators, from their basic function to maintenance tips, repair costs, and replacement options.
Join our: Whatsapp Group
Types of Car Radiators :
- Downflow Radiators: These are the most common type found in vehicles. In a downflow radiator, the coolant flows from the top tank to the bottom tank vertically, passing through the core and dissipating heat along the way.
- Crossflow Radiators: In crossflow radiators, the coolant flows horizontally across the core from one side to the other. This design allows for better cooling efficiency as the coolant has more contact with the tubes.
- Aluminum Radiators: Aluminum radiators are lightweight and offer better heat dissipation compared to traditional copper/brass radiators. They are commonly used in high-performance vehicles.
- Copper/Brass Radiators: These radiators consist of copper tubes and brass tanks. They are durable and offer good heat transfer properties but are heavier compared to aluminum radiators.
- Plastic Tank Radiators: These radiators feature plastic tanks instead of traditional metal tanks. They are lighter and less prone to corrosion but may not be as durable as metal tank radiators.
- Modular Radiators: Modular radiators allow for easier replacement of individual components such as the core or tanks, making maintenance and repairs more convenient.
- High-Efficiency Radiators: These radiators feature advanced designs and materials to improve cooling efficiency and reduce engine temperatures, often used in high-performance or racing applications.
- Dual Pass Radiators: Dual pass radiators have the coolant flow through the core twice before returning to the engine. This design enhances cooling efficiency, especially in applications where space is limited.
- Oil Cooler Integrated Radiators: Some radiators come with built-in oil coolers, especially in vehicles with performance or towing capabilities. These radiators help regulate the temperature of both engine coolant and engine oil.
- Electric Radiators: Electric radiators utilize electric fans to cool the coolant instead of relying solely on airflow from the vehicle’s motion. They are often used in applications where additional cooling is required, such as in high-performance or modified vehicles.
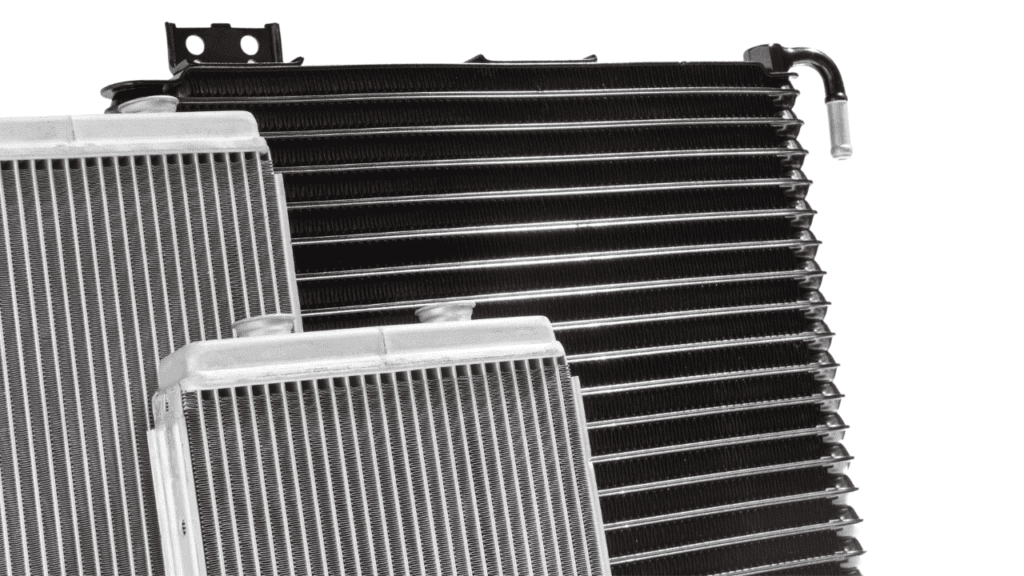
What Does a Car Radiator Do?
A car radiator is a vital component of the cooling system, responsible for dissipating heat generated by the engine during operation. As the engine burns fuel to produce power, it generates a significant amount of heat. Without proper cooling, this heat can cause the engine to overheat, leading to severe damage and potential breakdowns.
The function of the radiator involves the circulation of coolant, typically a blend of water and antifreeze, throughout the engine to soak up excess heat.This heated coolant then flows into the radiator, where it passes through a series of small tubes surrounded by fins. As air passes over these fins, heat is transferred from the coolant to the surrounding air, cooling it down before it is recirculated back into the engine.
In addition to cooling the engine, the radiator also helps regulate the operating temperature of other components, such as the transmission and power steering system, in some vehicles.
Must Read : Aluminium | Complete Details
How Does a Radiator Work in a Car?
Understanding the basic principles of how a radiator works is essential for proper maintenance and troubleshooting. Here’s a simplified explanation of the radiator’s operation:
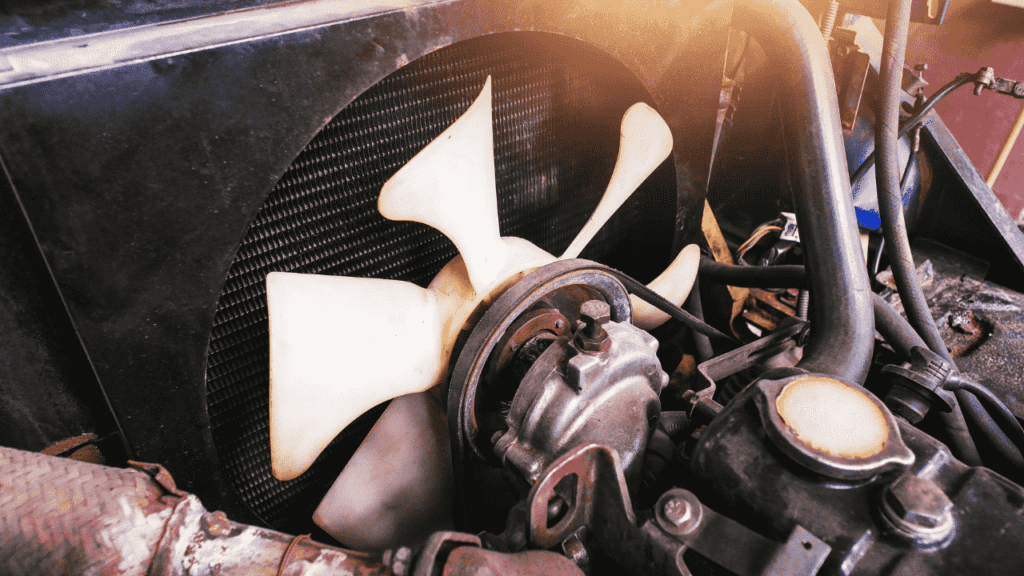
- Coolant Circulation: The cooling process begins when the engine reaches operating temperature, causing the thermostat to open and allow coolant to flow from the engine into the radiator.
- Heat Exchange: As the hot coolant enters the radiator, it travels through a network of small tubes with thin walls. These tubes are surrounded by fins, increasing the surface area for heat exchange.
- Airflow: As the vehicle moves or the cooling fan operates, air is forced through the radiator, removing heat from the coolant. The fins help distribute the heat evenly, maximizing cooling efficiency.
- Coolant Return: Once the coolant has been sufficiently cooled, it exits the radiator and returns to the engine to repeat the cooling cycle.
This continuous process ensures that the engine operates within the optimal temperature range, preventing overheating and maintaining peak performance.
Maintenance Tips for Car Radiators
Proper maintenance is key to ensuring the longevity and efficiency of your car’s radiator.Here are a few crucial pointers for maintaining your cooling system’s optimal performance:
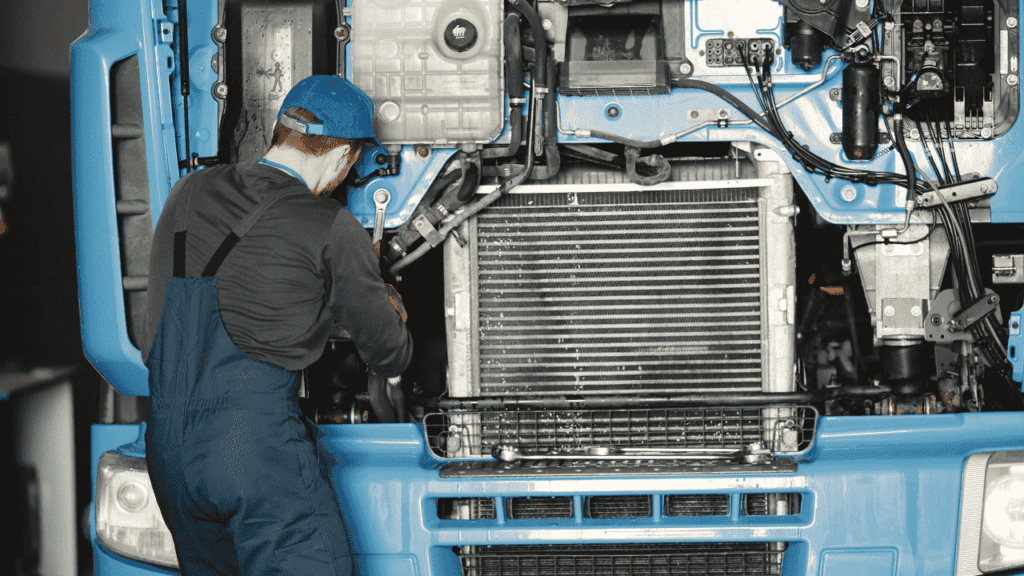
- Check Coolant Levels: Regularly inspect the coolant reservoir and top up as needed to maintain the proper level. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendation by utilizing a blend of coolant and distilled water for your cooling system.
- Inspect for Leaks: Periodically check for signs of coolant leaks around the radiator, hoses, and connections. Leaks can lead to a loss of coolant and compromise the cooling system’s effectiveness.
- Clean the Radiator: Over time, dirt, debris, and bugs can accumulate on the radiator fins, obstructing airflow. Use a soft brush or compressed air to gently clean the fins and ensure optimal cooling performance.
- Replace Hoses and Clamps: Inspect radiator hoses and clamps for signs of wear or deterioration, such as cracks or leaks. Replace any damaged components to prevent coolant leaks and potential engine damage.
- Flush the Cooling System: Periodically flush the cooling system to remove old coolant, debris, and contaminants. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the proper procedure and interval for flushing.
- Inspect the Radiator Cap: The radiator cap helps maintain the correct pressure in the cooling system. Inspect the cap for signs of wear or damage and replace it if necessary to prevent coolant leaks.
- Monitor Engine Temperature: Keep an eye on your vehicle’s temperature gauge while driving. If you notice any sudden spikes or fluctuations in temperature, it could indicate a problem with the cooling system that requires immediate attention.
By following these maintenance tips, you can help prevent costly repairs and ensure that your car’s radiator continues to operate efficiently.
Related :Brass | Complete Details
Common Car Radiator Issues and Repairs
Despite regular maintenance, car radiators can still develop problems over time.Here are several typical problems you might run into:

- Coolant Leaks: Leaking coolant is a common problem that can be caused by damaged hoses, loose connections, or a corroded radiator. If you notice puddles of coolant under your vehicle or a drop in coolant levels, have the system inspected for leaks.
- Clogged Radiator: Accumulated dirt, debris, or mineral deposits can clog the radiator, restricting airflow and impeding cooling. Flushing the radiator can help remove these obstructions and restore proper function.
- Radiator Damage: Physical damage to the radiator, such as bent fins or punctures, can impair its ability to dissipate heat effectively. In such cases, radiator repair or replacement may be necessary to prevent engine overheating.
- Thermostat Failure: A faulty thermostat can cause the engine to overheat by either staying closed, preventing coolant flow, or staying open, causing the engine to run too cool. Replacing the thermostat can effectively address this problem.
- Cooling Fan Problems: If the cooling fan fails to operate correctly, airflow through the radiator may be insufficient to cool the coolant effectively. This can lead to engine overheating, especially at low speeds or when idling.
- Corrosion and Rust: Over time, the inside of the radiator can corrode and develop rust, compromising its structural integrity and cooling efficiency. Flushing the cooling system regularly can help prevent corrosion and extend the radiator’s lifespan.
Car Radiator Replacement Cost
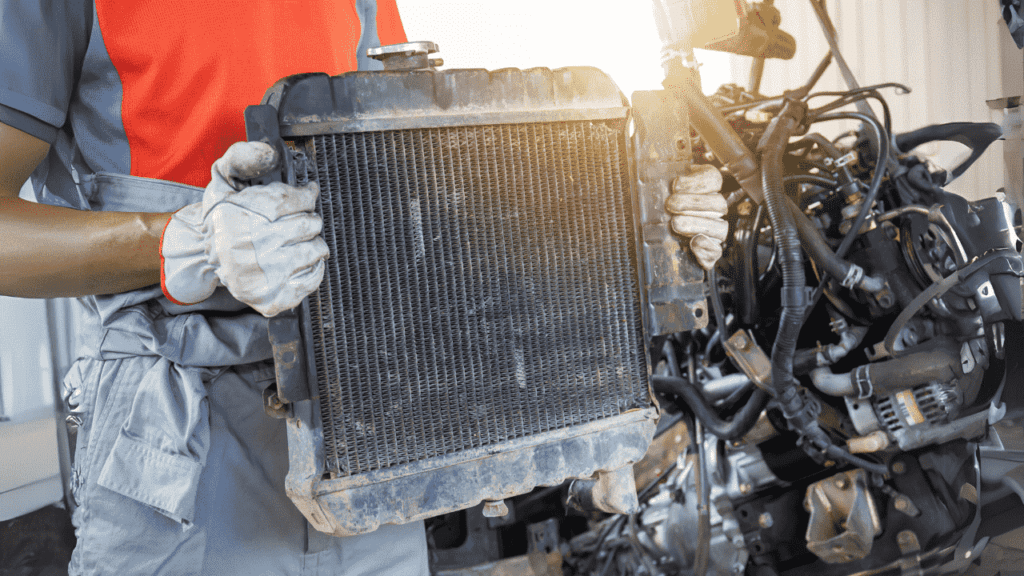
In some cases, repairing a damaged radiator may not be feasible, and replacement becomes necessary. The cost of replacing a car radiator can vary depending on several factors, including the make and model of the vehicle, the type of radiator, and labor costs. On average, however, you can expect to pay between $300 and $900 for parts and labor.
Table: Comparison of Car Radiator Replacement Costs
| Type of Radiator | Average Cost (Parts + Labor) |
|---|---|
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | $400 – $900 |
| Aftermarket | $300 – $700 |
| Performance Upgrade | $500 – $1500 |
Visit Our Prices Page For Latest Metals Rates
FAQs:
- What do car radiators do?
- Car radiators keep the engine cool by dissipating heat generated during operation.
- What are the main types of car radiators?
- The main types include downflow, crossflow, aluminum, copper/brass, plastic tank, modular, high-efficiency, dual pass, oil cooler integrated, and electric radiators.
- How do downflow radiators differ from crossflow radiators?
- Downflow radiators have vertical coolant flow, while crossflow radiators have horizontal flow, offering better cooling efficiency.
- Why choose aluminum radiators over copper/brass?
- Aluminum radiators are lighter and offer superior heat dissipation.
- Why are plastic tank radiators gaining popularity?
- They’re lighter and less prone to corrosion than metal tank radiators.
- What’s the benefit of modular radiators?
- Easier component replacement for maintenance.
- When are high-efficiency radiators used?
- Typically in high-performance or racing vehicles.
- Where are dual pass radiators commonly used?
- In compact cars or performance vehicles for enhanced cooling in limited space.
- How do oil cooler integrated radiators help?
- They regulate engine coolant and oil temperatures, improving performance.
- What sets electric radiators apart?
- They use electric fans for cooling, ideal for high-performance or modified vehicles.
Join our: Whatsapp Group
Conclusion
Your car’s radiator is a critical component of the cooling system, responsible for maintaining the engine’s operating temperature and preventing overheating. By understanding how radiators work and following proper maintenance practices, you can ensure that your vehicle stays cool and reliable for years to come. If you encounter any issues with your car radiator, don’t hesitate to seek professional assistance to diagnose and resolve the problem promptly. Remember, a well-maintained radiator is essential for the health and longevity of your vehicle.