Introduction
Your AC compressor is the silent hero behind the cool breeze on hot summer days. Understanding its inner workings, troubleshooting common problems, and implementing effective maintenance routines can ensure optimal performance and longevity for your air conditioning system.
Join our: Whatsapp Group
What is an AC Compressor?
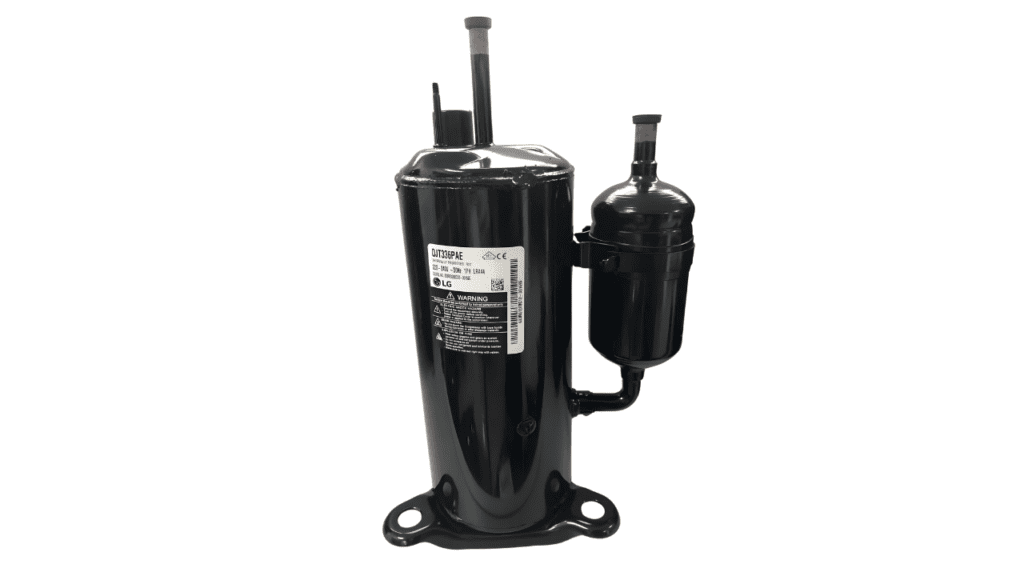

At the heart of your air conditioning system lies the AC compressor, a vital component responsible for pressurizing refrigerant gas, facilitating heat exchange, and cooling your indoor environment. This mechanical marvel compresses the refrigerant, transforming it into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas that releases heat outside, allowing cooler air to circulate indoors.
Types of AC Compressors
- Sanden AC Compressor: Widely utilized in automotive air conditioning systems, Sanden compressors are renowned for their reliability, efficiency, and compatibility with various vehicle models.
- 12V AC Compressor: Ideal for smaller vehicles, RVs, and portable cooling solutions, 12V compressors offer versatility and convenience.
- York AC Compressor: Known for their robust construction and suitability for larger cooling systems, York compressors excel in heavy-duty applications.
- Denso Compressor AC: Found in a multitude of vehicle makes and models, Denso compressors boast compact designs, superior performance, and industry-leading reliability.
- QP7H15 AC Compressor: Commonly employed in commercial trucks, buses, and industrial cooling units, QP7H15 compressors deliver high-volume cooling under demanding conditions.
Must Read : Copper | Complete Details
Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance is key to preserving your AC compressor’s functionality and efficiency:

- Clean or Replace Air Filters: Dirty filters restrict airflow, strain the compressor, and compromise indoor air quality. Replace or clean filters regularly to maintain optimal airflow and efficiency.
- Inspect and Clean Condenser Coils: Dirty or clogged condenser coils impede heat transfer, causing the compressor to work harder and consume more energy. Clean coils periodically to ensure efficient heat dissipation.
- Check Refrigerant Levels: Low refrigerant levels can lead to compressor overheating and failure. Schedule regular inspections and recharge refrigerant as needed to maintain optimal performance.
- Lubricate Moving Parts: Proper lubrication reduces friction and wear on compressor components, prolonging their lifespan and minimizing energy consumption.
- Inspect Electrical Components: Ensure electrical connections are secure, wires are intact, and components are free from corrosion or damage. Address any electrical issues promptly to prevent compressor failure.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even the most dependable AC compressors may encounter glitches over time. Here’s how to deal with some common problems:
- AC Compressor Cycles On and Off: If your compressor repeatedly cycles on and off every 5 seconds, it could indicate low refrigerant levels, a faulty thermostat, or a blocked airflow.
- AC Compressor Leaks: Keep an eye out for signs of refrigerant leaks, such as oil spots or hissing sounds near the compressor. Promptly address leaks to prevent reduced cooling efficiency and environmental harm.
- AC Compressor Won’t Turn On: Electrical problems, such as blown fuses, damaged wiring, or malfunctioning compressor clutches, can prevent the compressor from starting. Inspect and repair electrical components as needed.

Comparing AC Compressors and Condensers
While the AC compressor and condenser work in tandem to cool your space, they serve distinct functions:
- AC Compressor: Compresses refrigerant gas, raising its pressure and temperature to facilitate heat transfer from indoors to outdoors.
- AC Condenser: Receives high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant vapor from the compressor and cools it down, causing it to condense into a liquid state.
Related : Iron | Complete Details
AC Compressor Scrap: Recycling Valuable Components
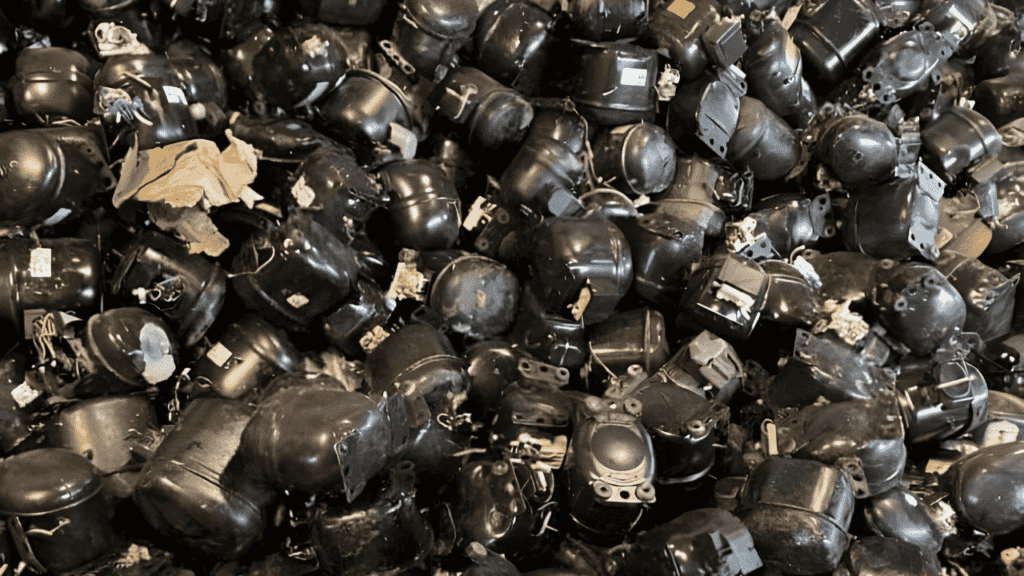

- Metal Content: Scrap AC compressors are rich sources of metals such as copper, aluminum, and steel. These metals are essential for various industrial applications and have high recycling value.
- Recycling Process: Scrap dealers and recycling centers dismantle AC compressors to extract the valuable metals. This process involves separating different components and sorting them based on their metal content.
- Environmental Impact: Recycling AC compressor scrap helps conserve natural resources by reducing the need for mining and manufacturing new metals. Additionally, recycling reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, thereby lowering environmental pollution.
- Economic Benefits: Selling AC compressor scrap to recycling centers provides individuals or businesses with a source of income. It also contributes to the economy by supporting the recycling industry and creating job opportunities.
- Safety and Regulations: Handling and transporting scrap materials, including AC compressors, require adherence to safety guidelines and local regulations. Proper precautions should be taken to ensure safety during dismantling, handling, and transportation processes.
- Community Engagement: Recycling AC compressor scrap fosters a sense of environmental responsibility within communities. By participating in recycling efforts, individuals and businesses contribute to a more sustainable future.
Comparison Table of Air And AC Compressors:
| Feature | Air Compressor | AC Compressor |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts power (usually electrical) into potential energy stored in compressed air | Converts refrigerant from low pressure to high pressure for cooling purposes |
| Application | Used in various industries for powering pneumatic tools, inflating tires, operating machinery, etc. | Essential component in air conditioning systems for cooling residential, commercial, and industrial spaces |
| Operation | Compresses atmospheric air to a desired pressure level | Compresses refrigerant gas to remove heat from indoor air |
| Pressure Output | Typically provides higher pressure outputs (measured in psi or bar) | Provides specific pressure levels required for refrigerant circulation (measured in psi or bar) |
| Cooling Requirement | Usually air-cooled, although some models may have water-cooling systems | Often equipped with dedicated cooling systems such as fans or refrigerant flow for efficient heat dissipation |
| Lubrication | Some models require lubrication for smooth operation | Often lubricated internally for reduced friction and wear |
| Size and Portability | Available in various sizes and configurations, from small portable units to large stationary units | Typically larger and stationary due to installation requirements in AC systems |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic maintenance such as oil changes, filter replacements, and inspection of hoses and fittings | Requires regular maintenance including cleaning, refrigerant level checks, and inspection of electrical components |
Visit Our Prices Page For Latest Metals Rates
FAQs:
1. What is an AC Compressor?
An AC compressor is a crucial component of your air conditioning system responsible for pressurizing refrigerant gas, facilitating heat exchange, and cooling your indoor environment.
2. What are the types of AC Compressors?
Different types include Sanden, 12V, York, Denso, and QP7H15 compressors, each suitable for specific applications ranging from automotive to industrial cooling.
3. Can I install any type of AC compressor in my air conditioning system?
It’s essential to choose a compressor compatible with your system’s requirements and specifications. Talking to an expert can help figure out what’s best for you.
4. How can I troubleshoot common AC compressor issues?
Common issues like frequent cycling, leaks, or failure to turn on can often be traced to factors like low refrigerant levels, electrical problems, or blocked airflow.
5. What maintenance tips can help optimize AC compressor performance?
Regularly cleaning or replacing air filters, inspecting and cleaning condenser coils, checking refrigerant levels, lubricating moving parts, and ensuring electrical components are in good condition are essential for optimal performance.
6. What’s the difference between AC compressors and condensers?
While compressors raise refrigerant pressure and temperature for heat transfer, condensers receive and cool down the high-pressure refrigerant vapor, causing it to condense into a liquid state.
7. How can I recycle AC compressor scrap?
Scrap AC compressors contain valuable metals like copper, aluminum, and steel, which can be recycled by dismantling them and extracting the metals. Recycling benefits the environment, economy, and community by conserving resources and reducing pollution.
8. Why is recycling AC compressor scrap important?
Recycling AC compressor scrap is economically beneficial, environmentally responsible, and socially impactful, contributing to resource conservation, pollution reduction, and community engagement.
9. What safety considerations are there when handling AC compressor scrap?
Handling and transporting scrap materials, including AC compressors, require adherence to safety guidelines and local regulations to ensure the well-being of individuals and the environment.
10. How can I ensure optimal performance and longevity for my air conditioning system?
Understanding AC compressor operation, identifying issues, implementing maintenance practices, and timely repairs are crucial for ensuring efficient cooling and energy savings.
Join our: Whatsapp Group
Conclusion
By understanding the fundamentals of AC compressor operation, identifying common issues, and implementing effective maintenance practices, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity for your air conditioning system. Regular maintenance and timely repairs will not only keep your space cool and comfortable but also contribute to energy savings and environmental sustainability.