Introduction
Copper, a versatile and essential metal, holds a significant place in human civilization due to its wide-ranging applications and historical significance. This comprehensive guide aims to explore various facets of copper, ranging from its properties, uses, historical significance, and industrial applications, to its environmental impact. By delving into the complete details of copper, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of this vital element and its crucial role in shaping our world. From its use in electrical wiring to its presence in ancient artifacts, copper’s importance spans across multiple industries and historical epochs. This detailed examination will provide valuable insights into the significance of copper in both past and present contexts, shedding light on its enduring relevance and importance in modern society.
Element Information :
Join our: Whatsapp Group
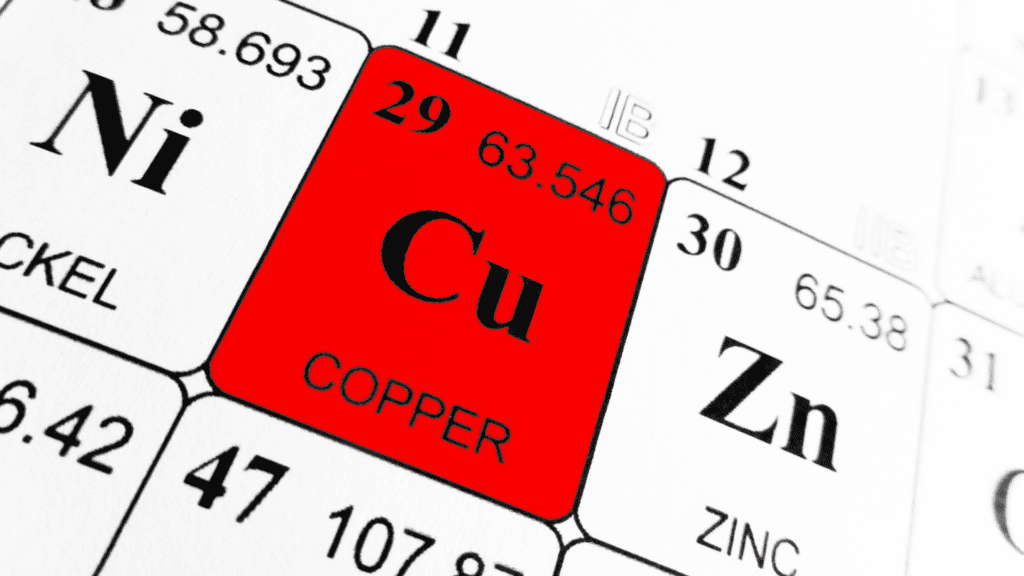
- Symbol: Cu
- Atomic Number: 29
- Atomic Mass: 63.546 u
- Electron Configuration: [Ar] 3d¹⁰ 4s¹
- Group: 11
- Period: 4
- Block: d
- Element Category: Transition Metal
- Color: Reddish-Brown
- Density: 8.96 g/cm³
- Melting Point: 1,984°F (1,084°C)
- Boiling Point: 5,301°F (2,927°C)
- Specific Heat Capacity: 0.385 J/g°C
- Electrical Conductivity: 59.6 × 10⁶ S/m
- Thermal Conductivity: 401 W/m·K
- Young’s Modulus: 110–128 GPa
- Shear Modulus: 48 GPa
- Bulk Modulus: 140 GPa
- Poisson Ratio: 0.34
- Mohs Hardness: 3
- Vickers Hardness: 369 MPa
- Brinell Hardness: 87–93 MPa
- Heat of Fusion: 13.26 kJ/mol
- Heat of Vaporization: 300.4 kJ/mol
- Oxidation States: +1, +2
Types of Copper :
Also Read :Top 5 Most Common Types of Metals and Their Uses
1. Pure Copper:
Also known as “Electrolytic Copper,” this is the highest purity level available. It’s prized for:
- Excellent electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Ideal for critical electrical applications.
- Used in wiring, conductors, and electrical components.
2. Copper Alloys:
Mixtures of copper with other metals, offering tailored properties:
- Bronze:
- Strong, durable alloy with a reddish-brown color.
- Commonly used in sculptures, bearings, and instruments.
- Brass:
- Golden-colored, corrosion-resistant alloy.
- Widely used in decor, plumbing, and fittings.
- Cupronickel:
- Offers excellent corrosion resistance in marine environments.
- Used in marine engineering, shipbuilding, and coinage.
- Beryllium Copper:
- High strength, hardness, and electrical conductivity.
- Used in aerospace, springs, connectors, and switches.
3. Recycled Copper:
Scrap copper, extensively recycled for sustainability:
- Preserves resources and reduces environmental impact.
- Retains properties, making it ideal for plumbing, construction, and electronics.
- Widely used in various applications, offering a sustainable choice.
Uses of Copper:
Visit Our Prices Page For Latest Metals Rates
- Electrical Wiring:
- Copper’s unparalleled conductivity makes it the standard choice for electrical wires and cables.
- Ensures efficient transmission of electricity in homes, buildings, and industrial settings.
- Construction and Architecture:
- Valued for its durability and corrosion resistance in plumbing pipes, roofing materials, and architectural elements.
- Used in building structures to enhance longevity and withstand environmental factors.
- Industrial Machinery:
- Bearings, gears, and heat exchangers benefit from copper’s strength and thermal conductivity.
- Ensures smooth operation and efficient heat transfer in machinery and equipment.
- Electronics and Telecommunications:
- Circuit boards, connectors, and switches rely on copper for reliable performance.
- Ensures stable connections and efficient signal transmission in electronic devices.
- Renewable Energy:
- Solar panels, wind turbines, and electric vehicle batteries incorporate copper for energy efficiency.
- Enhances the performance and longevity of renewable energy systems.
Effects Of Copper:
Must Read :LME : London Metal Exchange | Complete Details

Health Effects:
Antimicrobial Benefits:
- Fight Against Germs:
- Copper surfaces in hospitals and public places help kill harmful bacteria and viruses.
- This reduces the chances of infections spreading, keeping spaces cleaner.
Human Health Risks:
- Symptoms of Overexposure:
- Feeling sick to your stomach with nausea and vomiting.
- Upset stomach and diarrhea, especially with too much copper in the body.
- Long-term exposure can damage the liver and kidneys, which are vital organs.
Skin Contact Reactions:
- Skin Irritation and Rashes:
- Prolonged touching of copper can lead to itchy or red skin.
- Some people might even develop allergies to copper, causing skin problems
Environmental Effects:
Mining Impact:
- Damage to Nature:
- Mining copper can harm the land, destroying homes for plants and animals.
- Chemicals from mining can leak into the ground and water, harming the environment.
Air and Water Contamination:
- Polluting Our Air and Water:
- When we make copper, it releases smelly and harmful gases into the air.
- The water near copper mines can become dirty with chemicals, hurting fish and plants.
Side Effects:
Occupational Hazards:
- Keeping Workers Safe:
- People who work with copper need to be careful.
- They have rules to follow to protect them from breathing in copper dust or fumes.
Consumer Product Risks:
- Watch Out in Your Kitchen:
- Copper pots and pans can sometimes make food taste funny, especially acidic foods like tomatoes.
- If too much copper gets into your food, it can make you sick.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Rules to Follow:
- Governments make rules to keep us safe from too much copper.
- They tell companies how much copper is okay to have in the air, water, and products we use.
Discovery and Future Of Copper :
Join our: Whatsapp Group
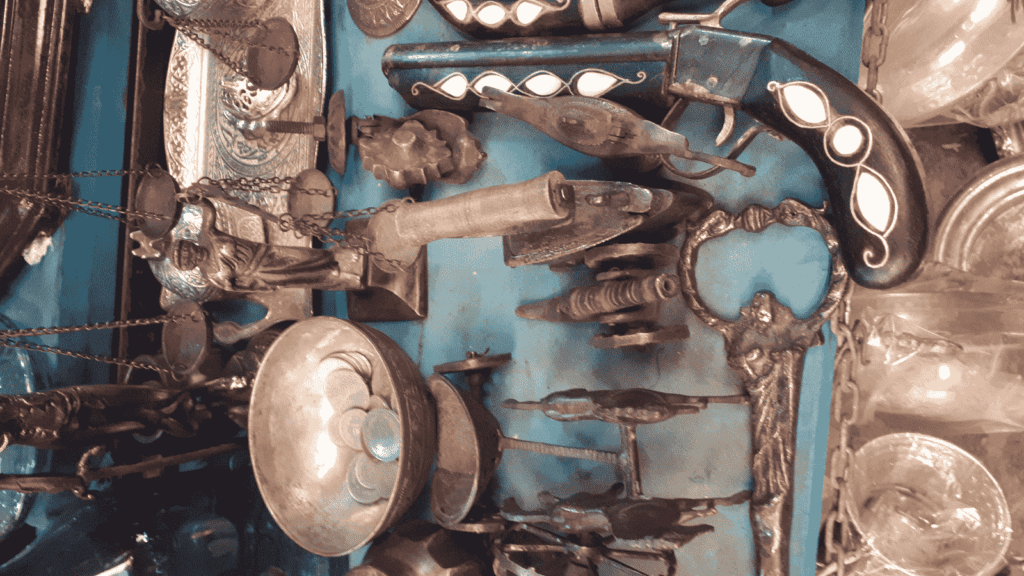

Discovery of Copper
Ancient Origins:
- Early Discoveries:
- Humans have known about copper for thousands of years.
- Ancient civilizations like the Egyptians and Mesopotamians used copper for tools, weapons, and art.
Copper Age:
- Birth of a Metal Age:
- The identification of copper signaled the dawn of the Copper Age.
- This era saw the widespread use of copper tools and artifacts.
Archaeological Finds:
- Historical Artifacts:
- Archaeologists find copper objects in ancient tombs and ruins.
- These artifacts give us clues about how ancient people used copper in their lives.
Future of Copper
Growing Demand:
- Rising Needs:
- As technology advances, so does the need for copper.
- It’s crucial for making electronics, from smartphones to electric cars.
Renewable Energy:
- Powering the Future:
- Copper plays a vital role in renewable energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines.
- These technologies rely on copper for efficient energy conversion.
Sustainable Mining:
- Responsible Practices:
- Mining companies are adopting eco-friendly methods to extract copper.
- This includes reducing waste, using less energy, and restoring mined areas.
Technological Innovations:
- Advancements Ahead:
- Scientists are finding new uses for copper in medical devices and construction materials.
- The future holds exciting possibilities for copper’s role in our lives.
Chemical Properties of Copper:
Related : latest Iron Scrap Rate Today
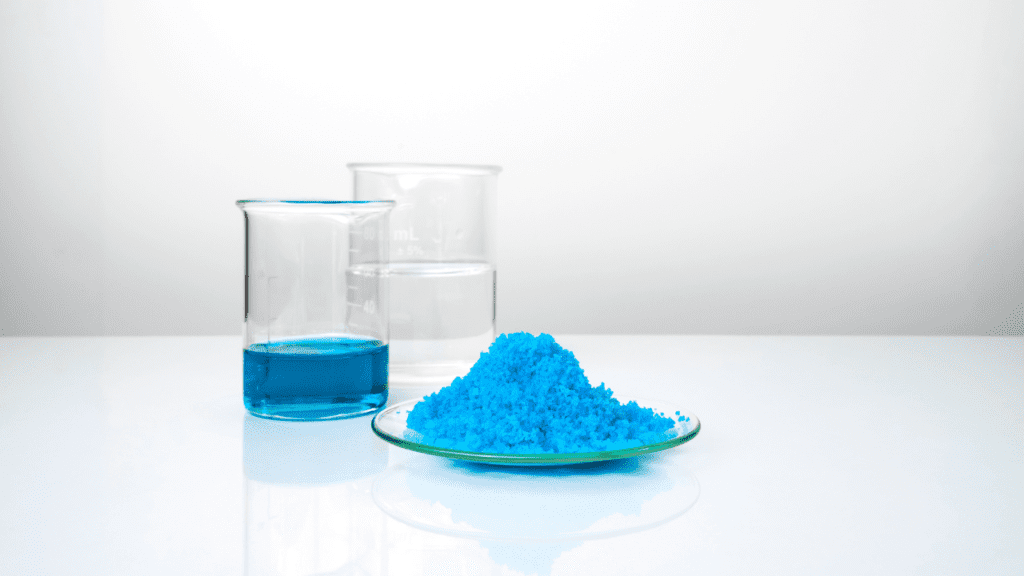

Corrosion Resistance:
- Protection Against Rust:
- Copper is highly resistant to corrosion, making it suitable for outdoor and marine environments.
- This property ensures that copper materials retain their strength and integrity over time.
Oxidation Reactions:
- Formation of Patina:
- When exposed to air and moisture, copper undergoes oxidation.
- This process results in the formation of a greenish patina, known as verdigris, on its surface.
Acid Reactions:
- Reaction with Acids:
- Copper reacts with acids such as sulfuric acid to form copper sulfate.
- The reaction additionally yields hydrogen gas as a byproduct.
Alloy Formation:
- Versatile Alloying Agent:
- Copper readily forms alloys with various metals, enhancing its properties.
- Alloys like bronze (copper and tin) and brass (copper and zinc) offer improved strength and corrosion resistance.
Conductivity Retention:
- Stable Electrical Conductivity:
- Even when oxidized, copper maintains its high electrical conductivity.
- This property is crucial for the efficient transmission of electricity in wires and cables.
Heat Transfer Capability:
- Efficient Thermal Conductivity:
- Copper’s ability to conduct heat makes it valuable in heat exchangers and cooling systems.
- It ensures efficient heat dissipation and temperature regulation in various applications.
Solubility and Stability:
- Limited Solubility:
- Copper has low solubility in water, contributing to its longevity in aqueous environments.
- This property makes it suitable for plumbing systems and water-related applications.
Catalytic Potential:
- Chemical Catalyst:
- Copper possesses the ability to serve as a catalyst in specific chemical reactions.
- Its presence can facilitate reactions, such as the oxidation of organic compounds.
Benefits and Importance Of Copper:
Also Read : Tamba Kiya Hota Hai? | Complete Details
Benefits of Copper
Excellent Conductivity:
- Efficient Electricity Flow:
- Copper ranks among the most efficient conductors of electricity.
- This makes it ideal for wiring homes, buildings, and electrical devices.
Heat Transfer:
- Effective Thermal Conductivity:
- Copper quickly transfers heat, making it useful in cooling systems and heat sinks.
- Helps in keeping electronics and machinery from overheating.
Durability and Longevity:
- Sturdy and Resilient:
- Copper exhibits resistance to corrosion, rust, and abrasion.
- Products made with copper last a long time, reducing the need for replacements.
Importance of Copper
Industrial Applications:
- Versatile Metal:
- Copper is essential in manufacturing industries for machinery, tools, and equipment.
- Used in construction for pipes, fittings, and structural components.
Electronics and Technology:
- Heart of Innovation:
- Vital for producing electronic devices like smartphones, computers, and TVs.
- The backbone of telecommunications systems, ensuring reliable connectivity.
Renewable Energy Support:
- Green Energy Backbone:
- Copper is crucial in solar panels and wind turbines, capturing and converting energy.
- Enables the transition to cleaner and sustainable energy sources.
Scrap and Recycling of Copper:
Join our: Whatsapp Group
Importance of Recycling:
- Resource Conservation:
- Recycling copper reduces the need for new mining, preserving natural resources.
- Helps in minimizing the environmental impact of extracting raw materials.
Process of Recycling:
- Collection and Sorting:
- Scrap copper is collected from various sources such as old wiring, plumbing, and electronics.
- Sorted into different grades based on purity and quality.
Melting and Purification:
- Smelting the Scrap:
- Scrap copper is melted in furnaces at high temperatures to remove impurities.
- This process separates the pure copper from other metals and materials.
Refining and Production:
- Creating New Copper Products:
- The purified copper is then refined to achieve the desired quality and properties.
- Used to produce new copper products such as wires, tubes, and sheets.
Benefits of Recycling:
- Energy Savings:
- Recycling copper consumes significantly less energy compared to producing new copper from ore.
- Decreases greenhouse gas emissions and aids in the fight against climate change.
Economic Impact:
- Job Creation and Revenue:
- Recycling industries create jobs in collection, processing, and manufacturing.
- Generates revenue from selling recycled copper to industries needing raw materials.
Environmental Advantages:
- Reduction in Landfill Waste:
- Recycling keeps copper out of landfills, reducing waste and environmental pollution.
- Helps in conserving landfill space for non-recyclable materials.
Applications of Recycled Copper:
- Manufacturing and Construction:
- Recycled copper is used in manufacturing processes for new products.
- Finds applications in building construction, plumbing systems, and electrical components.
Circular Economy Approach:
- Closing the Loop:
- Recycling copper creates a sustainable cycle where materials are reused indefinitely.
- Supports the concept of a circular economy, reducing the need for extracting new resources.
Challenges and Innovations:
- Technological Advances:
- Innovations in recycling technology improve efficiency and reduce waste in the process.
- Challenges include sorting mixed materials and handling contaminated scrap.
Visit Our Prices Page For Latest Metals Rates
FAQs :
1. Why is copper used in wires?
Copper is used in wires because it helps electricity move very well. This means our homes, buildings, and machines can have electricity easily.
2. Does copper help keep things clean?
Yes, copper can kill harmful germs. So, when we use things like copper doorknobs or hospital surfaces, they can help stop germs from spreading.
3. How does copper help with clean energy?
Copper is important for things like solar panels and wind turbines. It helps these devices turn sunlight and wind into electricity we can use.
4. Can too much copper be bad for our bodies?
Yes, if we have too much copper in our bodies, it can make us feel sick. It might give us a tummy ache, make our skin itchy, or even hurt our liver and kidneys.
5. Is mining copper bad for nature?
Mining for copper can harm the land, plants, and animals. It can also make the air and water near mines dirty, which is bad for the environment.
6. Why is recycling copper good?
Recycling copper helps us use less new copper, saving resources. It also stops old copper from filling up landfills, which is better for our planet.
7. What are the challenges in recycling copper?
Sometimes it’s hard to separate different materials mixed with copper. Also, making sure recycled copper is clean and pure can be tricky.
8. What are the different types of copper mixes and where are they used?
There are mixes like bronze and brass. Bronze is strong and used in things like sculptures, while brass is golden and good for decor and plumbing.
9. How does copper help machines stay cool?
Copper can move heat quickly, so it’s used in machines to keep them from getting too hot. This helps them work well without overheating.
10. Can copper affect the taste of food?
Yes, copper pots and pans can make food taste different, especially acidic foods like tomatoes. It’s important to use them correctly.
11. Why is copper good for pipes?
Copper pipes are great because they don’t rust, they last a long time, and they can even help keep the water clean.
12. How does copper make our gadgets work better?
Copper helps our phones, computers, and other gadgets send signals well. This means we get good internet and clear calls because of copper.
Also Read :Certified Scrap Brass Shells Recycler
Conclusion: Unveiling the Versatility and Significance of Copper
Copper, a metal steeped in history and innovation, emerged as a cornerstone of human civilization through its myriad applications and enduring qualities. From ancient civilizations to modern technological marvels, copper has left an indelible mark on our world.
Exploring the complete details of copper reveals a metal of remarkable properties. Its distinct reddish-brown hue and metallic luster beckon attention, while its atomic structure showcases a wealth of characteristics. As a transition metal with atomic number 29, copper boasts exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, making it an essential material in countless industries.
Delving deeper, the chemical properties of copper unveil its corrosion resistance, oxidation reactions, and versatile alloying capabilities. Whether as an efficient conductor of electricity or a reliable thermal conductor, copper stands at the forefront of modern technological advancements.
The myriad uses of copper paint a picture of versatility and indispensability. From wiring our homes to forming the backbone of telecommunications, copper ensures the efficient flow of energy and information. Its role in construction, industrial machinery, and renewable energy solutions highlights its durability and longevity.
However, the benefits of copper come with considerations. Health effects, environmental impacts, and occupational hazards underscore the need for responsible usage and disposal. While its antimicrobial properties combat harmful pathogens, improper handling can lead to adverse health reactions.
The future of copper shines bright with promise. As we embrace renewable energy sources and sustainable practices, copper stands poised to power this transition. Technological innovations continue to push the boundaries of its applications, from medical devices to construction materials.
Recycling emerges as a vital aspect of copper’s lifecycle, offering energy savings, economic benefits, and environmental stewardship. Through efficient recycling processes, we create a circular economy where copper finds new life in perpetuity.
In conclusion, the journey through the world of copper reveals a metal of unparalleled significance. Its properties, applications, and environmental considerations paint a holistic picture of a metal that has shaped civilizations and continues to drive progress. From the ancient Egyptians to the cutting-edge technologies of today, copper remains a steadfast companion in our journey towards a sustainable and innovative future.